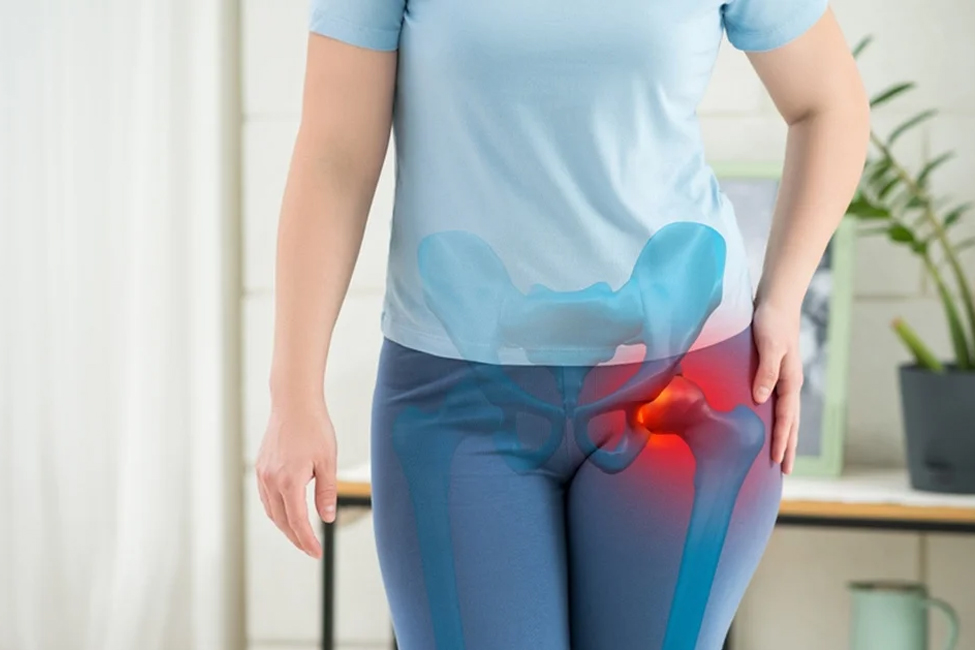
The transformative hip replacement is designed to alleviate pain and restore function. Our orthopaedic specialists at TOPS provide insight into hip replacement surgery, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your health. Explore key aspects, including the procedure and recovery expectations.
What Is Hip Replacement?
Hip replacement, or hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to alleviate chronic hip pain and improve mobility. This intervention is commonly recommended for individuals facing arthritis, joint damage, or injuries affecting the hip joint. During the surgery, the damaged or worn-out parts of the hip joint are replaced with artificial components, enhancing overall joint function and reducing pain. This procedure aims to restore your ability to perform daily activities with greater ease, ultimately contributing to an improved quality of life.
Conditions Requiring Hip Replacement
Hip replacement surgery, or hip arthroplasty, is often recommended to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with severe hip joint problems. Here are some common reasons why someone might undergo hip replacement:
Osteoarthritis
This is the most common reason for hip replacement surgery. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the hip joint to wear away over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of the synovium, the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints. Over time, this inflammation can damage the cartilage and bones in the hip joint, necessitating hip replacement surgery.
Avascular Necrosis
Avascular necrosis is a condition where the blood supply to the hip joint is compromised, leading to the death of bone tissue. This can result in severe pain and the collapse of the hip joint, requiring surgical intervention.
Hip Fractures
Hip joint fractures, especially in older individuals, may be treated with hip replacement surgery if the fracture is severe and not amenable to other forms of treatment.
Hip Dysplasia
This condition is where the hip socket is abnormally shallow, causing instability and accelerated joint wear. Hip replacement may be recommended to improve joint stability and function.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine, but it can also involve the hips. Hip replacement surgery may be considered if the hip joints are significantly affected, and conservative treatments are ineffective.
Traumatic Arthritis
Severe joint injuries or fractures resulting from arthritis over time may require hip replacement surgery to alleviate pain and restore function.
Tumours
Tumours in or around the hip joint may necessitate the removal of the affected joint and its replacement with an artificial one.
Failed Previous Surgeries
Individuals may undergo hip replacement surgery if previous hip surgeries, such as hip resurfacing or partial hip replacement, have failed to provide relief or have resulted in complications.
Preparing For Hip Replacement
Preparing for hip replacement surgery or hip arthroplasty involves several steps to ensure that you are physically and mentally ready for the procedure and the following recovery period. Here are some general guidelines to help you prepare:
Pre-surgery Planning
- Consultation with the Surgeon: Schedule a consultation with your orthopaedic surgeon to discuss the details of the surgery, including the risks and benefits.
- Medical Evaluation: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation to assess your overall health and identify any potential issues that may affect the surgery or recovery.
- Communication with the Healthcare Team: Communicate openly with your healthcare team about your medical history, current medications, and any allergies.
- Education: Learn about the procedure, expected outcomes, and the recovery process. This can help you set realistic expectations and mentally prepare for the surgery.
Preoperative Preparation
- Preoperative Exercises: Your surgeon or physical therapist may recommend specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around your hip joint before hip arthroplasty. This can help improve postoperative recovery.
- Weight Management: If you are overweight, consider working on weight management before surgery. Losing excess weight can reduce stress on the hip joint and improve surgical outcomes.
- Home Modification: Make necessary modifications to your home to create a safe and accessible environment for your recovery. This may include installing handrails, raising toilet seats, and removing trip hazards.
- Assistive Devices: Obtain any assistive devices recommended by your healthcare team, such as crutches, a walker, or a cane—practice using these devices before the surgery.
- Arrangements for Assistance: Arrange for someone to assist you during the initial days of recovery. This may include help with household chores, transportation to medical appointments, and emotional support.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting before the surgery. Smoking can impair healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Alcohol and Medication Review: Discuss with your healthcare team any medications or supplements you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs. Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before surgery.
Preoperative Screening
- Preoperative Testing: Complete any preoperative tests your healthcare team recommends, such as blood tests, X-rays, or electrocardiograms.
- Infection Prevention: Follow guidelines to reduce the risk of infection, such as proper wound care, dental hygiene, and avoiding sick contacts in the weeks leading up to surgery.
Types Of Hip Replacement Procedures
There are different types of hip replacement procedures, and the choice of the specific technique depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition, the surgeon’s preference, and the nature of the hip joint problem. Here are some common types of hip replacement procedures:
Total Hip Replacement (THR)
In a total hip replacement, the femoral head (the ball) and the acetabulum (the socket) are replaced with artificial components. This is the most common type of hip replacement surgery.
- Complete Replacement Of The Hip Joint: Total hip replacement involves the comprehensive replacement of the damaged hip joint with a prosthesis. This procedure addresses widespread joint deterioration, providing long-term relief from pain and improved functionality.
- Materials Used In The Artificial Joint: The artificial joint components are typically crafted from durable metal, plastic, or ceramic materials. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand the demands of daily activities, ensuring the longevity and stability of the replaced hip joint.
Partial Hip Replacement (Hemi-arthroplasty)
Only the femoral head is replaced in a partial hip replacement, and the natural acetabulum is retained. This procedure is often performed in fractures or other conditions where only part of the hip joint is damaged.
- Replacement Of Only The Damaged Part Of The Hip Joint: Unlike total hip replacement, partial hip replacement focuses on replacing only the damaged or deteriorated portion of the hip joint. This procedure is often considered when the damage is confined to a specific area, preserving more of the natural joint.
- Suitable Candidates For Partial Hip Replacement: Candidates for partial hip replacement are individuals with localised joint damage, usually in the femoral head or neck. This approach is considered when preserving the healthy portions of the hip joint is viable, offering a more conservative option for certain patients.
Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement
Minimally invasive techniques involve smaller incisions and less disruption of surrounding tissues compared to traditional total hip replacement. This approach aims to reduce postoperative pain and speed up recovery.
Anterior Approach Total Hip Replacement
In the anterior approach, the hip joint is accessed from the front of the hip rather than the side or back. This method may result in less muscle damage and a faster recovery.
Posterior Approach Total Hip Replacement
The posterior approach involves accessing the hip joint from the back. It is a traditional approach but may involve cutting through muscles, potentially leading to a longer recovery.
Hip Resurfacing
In hip resurfacing, only the surface of the hip joint is replaced rather than removing the entire femoral head. This option is sometimes considered for younger, active patients. However, it has become less common due to concerns about complications.
Revision Hip Replacement
Revision hip replacement is performed to replace a failed or worn-out artificial hip joint. This may involve replacing one or more components of the prosthetic joint.
Bilateral Hip Replacement
Some individuals may require hip replacement on both sides (bilateral hip replacement). The surgeries can be done simultaneously or in separate procedures.
Cemented vs. Uncemented Hip Replacement
The artificial components are fixed in place using bone cement in cemented hip replacement. In an uncemented hip replacement, the components rely on the natural bone to grow into the implant for stability.
Hybrid Hip Replacement
Hybrid hip replacement combines cemented and uncemented components, such as cemented femoral and uncemented acetabular components.
The Hip Replacement Surgery Process
The hip replacement surgery typically involves several key stages, ensuring a comprehensive and successful procedure.
Preoperative Evaluation
Before the surgery, you will undergo a thorough medical evaluation to assess your health and identify potential risks. Your orthopaedic surgeon will review your medical history, conduct physical examinations, and order imaging tests to precisely understand the condition of your hip joint.
Preparation for Surgery
Your surgeon will provide guidelines to prepare for the surgery, including lifestyle adjustments and potential medications. Preoperative exercises may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the hip, facilitating a smoother recovery.
Anesthesia and Incision
On the day of surgery, you will receive anaesthesia to ensure a pain-free experience. The surgeon then makes an incision to access the hip joint. The size and location of the incision may vary based on the specific surgical approach chosen.
Hip Joint Resurfacing or Replacement
In total hip replacement, the damaged portions of the hip joint are removed and replaced with artificial components. These components, made of durable materials, mimic the hip’s natural movement. In partial hip replacement, only the damaged part of the joint is replaced, preserving the healthy portions.
Wound Closure
Once the replacement or resurfacing is completed, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples. The wound is then dressed, and you are moved to a recovery area.
Postoperative Recovery
You will be closely monitored for complications during the initial recovery period. Physical therapy is often initiated to help you regain strength and mobility. Pain management strategies are employed to ensure your comfort.
Hospital Stay and Follow-up Care
The length of hospital stay varies but typically ranges from a few days to a week. After discharge, a comprehensive follow-up plan, including physical therapy and regular check-ups, is established to monitor your progress and address concerns.
Recovery And Rehabilitation
Recovery and rehabilitation following hip replacement surgery are crucial phases in restoring mobility and ensuring the long-term success of the procedure.
- Your hospital stay, typically lasting a few days to a week, involves working with physical therapists to improve joint mobility and strength.
- Medications are prescribed for pain relief, with adjustments made as needed during the initial recovery.
- Once home, follow the surgeon’s instructions for wound care and medications and gradually resume activities with outpatient physical therapy.
- Over weeks, resume daily activities with the help of physical therapy, starting with assistive devices and transitioning to independent walking.
Focus on endurance, flexibility, and joint function in long-term rehabilitation, tailored to your needs. - Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon, including X-rays, are crucial for monitoring progress and addressing concerns.
- Make lifestyle adjustments such as maintaining a healthy weight and incorporating joint-friendly exercises for a successful recovery.
Schedule Your Appointment Now
For those considering hip replacement, it’s important to recognise that this transformative journey can significantly improve your quality of life. The strides in medical technology and the expertise of our orthopaedic specialists at TOPS ensure a comprehensive and personalised approach to your care.
If you’re grappling with persistent hip pain or diminished mobility, take the first step towards a brighter future. Seek professional advice from our experienced team. From informative consultations to procedures, we are dedicated to guiding you toward renewed vitality and well-being.
Don’t let hip discomfort hinder your daily activities any longer. Embrace the possibilities that hip replacement can offer. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and embark on a journey towards a more active, pain-free life. Your improved mobility and comfort are just a call away.