Hip Labral Tear: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is a Labral Tear?
A labral tear refers to damage or injury to the labrum, a ring of cartilage surrounding the socket part of the joint. Labral tears often occur in the hip or shoulder joint, leading to pain, discomfort, and potential limitations in joint movement.
Types of Labral Tear
- Shoulder Labral Tears: Commonly caused by acute injury, repetitive motion, or dislocations, resulting in pain, weakness, or instability in the shoulder.
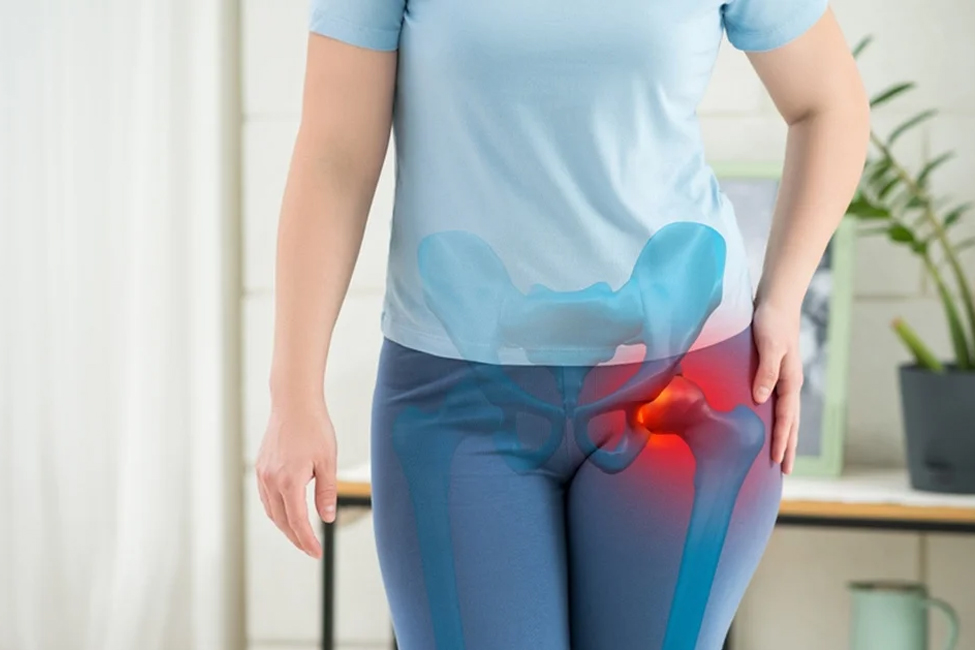
- Hip Labral Tears: Often due to structural abnormalities or repetitive stress, causing hip pain, limited range of motion, or a feeling of catching or locking in the joint.
How Common is Labral Tear?
Labral tears are relatively common, particularly in athletes or individuals involved in activities that stress the shoulder or hip joint. In the shoulder, labral tears are often seen in overhead athletes (like baseball pitchers).
At the same time, in the hip, they’re common in athletes engaged in activities involving frequent hip movements (like runners or dancers). Additionally, degenerative changes with age might also contribute to labral tears.
Causes of Hip Labral Tear
Hip labral tears can result from various factors, including:
- Structural Abnormalities: Anatomic irregularities in the hip joint, such as femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) or hip dysplasia, can lead to increased friction, wear, and tear on the labrum.
- Trauma or Injury: Acute injuries, such as falls, accidents, or sudden impacts, can cause damage to the hip labrum.
- Repetitive Movements or Stress: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive hip movements or high impact on the joint, such as certain sports or occupations, can contribute to the development of labral tears.
- Degenerative Changes: Over time, natural wear and tear on the hip joint due to ageing can lead to degeneration of the labrum, making it more susceptible to tears.
Symptoms of Hip Labral Tear
Symptoms of a hip labral tear can vary but commonly include:
- Hip Pain: Dull or sharp pain in the groin or outer hip area, often worsened by prolonged sitting, walking, or specific movements.
- Catching or Locking Sensation: Feeling of the hip “catching” or “locking” during certain movements, such as getting up from a chair or rotating the hip.
- Stiffness or Limited Range of Motion: Reduced flexibility in the hip joint, leading to stiffness or limitations in movement.
- Clicking or Popping: Some individuals might experience clicking, popping, or grinding sensations in the hip joint during movement.
- Instability or Weakness: Feeling of instability or weakness in the hip joint, affecting mobility and overall function.
Diagnosis of Hip Labral Tear
Diagnosing a hip labral tear typically involves a combination of approaches:
Medical History
A discussion about the individual’s symptoms, their nature, duration, and any previous injuries or hip discomfort.
Physical Examination
A comprehensive evaluation of the hip joint, assessing range of motion, stability, and signs of discomfort or pain during specific movements.
Imaging Tests
Various imaging techniques can assist in diagnosis, including:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the soft tissues, helping identify tears or damage to the labrum.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Offers 3D imaging to assess structural abnormalities or bone conditions related to the labral tear.
Diagnostic Hip Arthroscopy
Sometimes, a minimally invasive arthroscopy procedure may be employed to directly visualise the hip joint, confirm the diagnosis, and potentially treat the tear.
Complications of Hip Labral Tear
Complications that may arise from a hip labral tear include:
- Chronic Pain: If left untreated or undiagnosed, a hip labral tear can lead to persistent discomfort and chronic pain in the hip joint.
- Hip Joint Instability: Severe tears or significant damage to the labrum can compromise the stability of the hip joint, affecting mobility and function.
- Increased Risk of Osteoarthritis: Long-term hip labral tears, especially if not managed, might contribute to the development or progression of osteoarthritis in the hip joint.
- Functional Limitations: Severe tears can result in limitations in daily activities, sports participation, or work-related tasks, affecting overall quality of life.
Treatment Options for Hip Labral Tear
Treatment options for a hip labral tear may involve both non-surgical and surgical approaches based on the severity of the tear and the patient’s specific situation:
Conservative Management
- Activity Modification: Avoiding movements that exacerbate symptoms and minimising high-impact activities.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in exercises to strengthen the hip muscles, improve joint stability, and enhance flexibility.
- Pain Management: Using anti-inflammatory medications or injections to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Arthroscopic Surgery
- Debridement: Trimming or smoothing the torn or damaged area of the labrum to reduce friction and discomfort.
- Labral Repair: Suturing the torn labrum back to its normal position to restore joint function and stability.
- Labral Reconstruction: In cases of severe tears, reconstructive procedures using tissue grafts or advanced techniques may be necessary.
Preventing Hip Labral Tear
Preventing a hip labral tear involves several strategies aimed at reducing the risk of injury:
- Engage in exercises that strengthen the hip joint and surrounding muscles. Emphasise a balanced exercise routine to improve joint stability and flexibility.
- Whether in sports or daily activities, use the correct techniques to reduce unnecessary stress on the hip joint.
- Limit activities that place excessive stress on the hip joint, especially those involving repetitive or high-impact movements.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the hip joint and lower the risk of developing joint problems.
- Attend regular check-ups and promptly address concerns about hip discomfort or unusual sensations to prevent potential injuries.
Living with Hip Labral Tear
Living with a hip labral tear may involve various considerations:
- Following the recommended treatment plan is essential for managing the condition and improving joint health.
- Adjusting daily activities and exercises based on orthopaedic specialist recommendations to minimise discomfort and prevent further injury.
- Engaging in specific exercises and physical therapy to enhance hip joint strength, stability, and flexibility, as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Continuing regular follow-ups with an orthopaedic specialist to monitor the condition and address any changes or concerns.
- Make modifications in daily routines or activities to accommodate any discomfort or limitations caused by the injury.
Hip labral tears can significantly impact joint health and overall well-being, leading to discomfort, reduced mobility, and potential complications if left untreated. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, coupled with lifestyle adjustments, are pivotal in managing such injuries and preventing long-term joint damage.
For personalised evaluation, effective treatment, and expert guidance specific to hip labral tears, consider seeking an appointment with The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic. Our specialised team can offer tailored assessments and effective strategies to address hip joint concerns, promoting better joint health and an improved quality of life.
Take the proactive step—request an appointment today to receive specialised care and guidance for hip labral tears from experienced professionals at The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic.