Rotator Cuff Tear: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
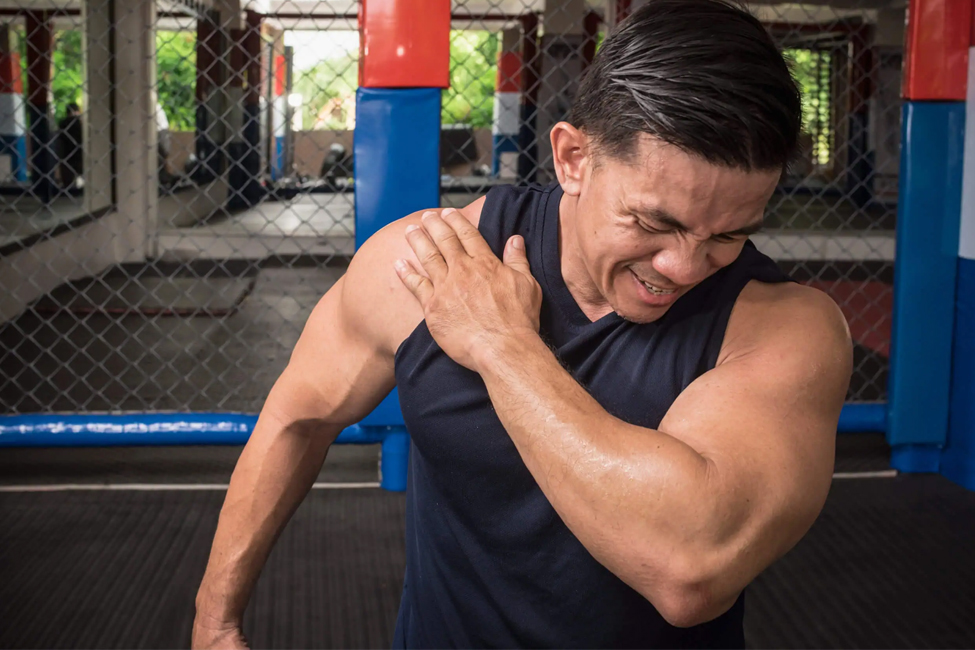
A rotator cuff tear is a common injury that affects the group of tendons and muscles in the shoulder joint known as the rotator cuff. These tendons and muscles are crucial in stabilising and moving the shoulder. A tear in the rotator cuff can range from a partial tear to a complete rupture, leading to pain, weakness, and limited shoulder function.
Type of Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator cuff tears can be classified into two main types based on the extent of the tear:
- Partial Tear: In a partial tear, only a portion of the tendon or muscle is damaged.
- Full-Thickness Tear: This type involves a complete tear or rupture of the tendon or muscle, which can significantly impact shoulder function.
How Common is Rotator Cuff Tear?
Rotator cuff tears are relatively common, particularly as individuals age. They can result from various causes, including age-related degeneration, overuse, or acute injuries. It’s estimated that millions of people experience rotator cuff tears each year, making it a prevalent shoulder condition.
Causes of Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator cuff tears can occur due to various factors, including:
- Ageing: The natural ageing process can lead to degeneration and weakening of the rotator cuff tendons, making them more susceptible to tears.
- Overuse: Repetitive overhead arm movements, common in sports or certain occupations, can lead to overuse injuries and tears.
- Acute Injuries: A sudden impact, fall, or traumatic event can cause an acute tear in the rotator cuff.
- Lifting Heavy Objects: Lifting heavy objects with improper form or straining the shoulder can contribute to rotator cuff tears.
- Impingement: Repeatedly pinching of the rotator cuff tendons between the shoulder bones can lead to tears over time.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tear
If you have a rotator cuff tear, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Shoulder Pain: The most common symptom is persistent shoulder pain, which may be a deep ache or sharp discomfort.
- Weakness: You may notice weakness in the affected arm, making performing tasks like lifting or reaching challenging.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving your arm, particularly overhead or behind your back, due to the tear’s impact on shoulder mobility.
- Pain at Night: Many individuals experience increased pain at night, which can disrupt sleep.
- Cracking or Popping Sounds: Some may hear or feel cracking or popping sensations when moving their shoulder.
Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tear
Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tear
Diagnosing a rotator cuff tear typically involves the following steps:
Medical History
Your orthopaedic specialist will ask about your symptoms, including the nature of the pain and when it began.
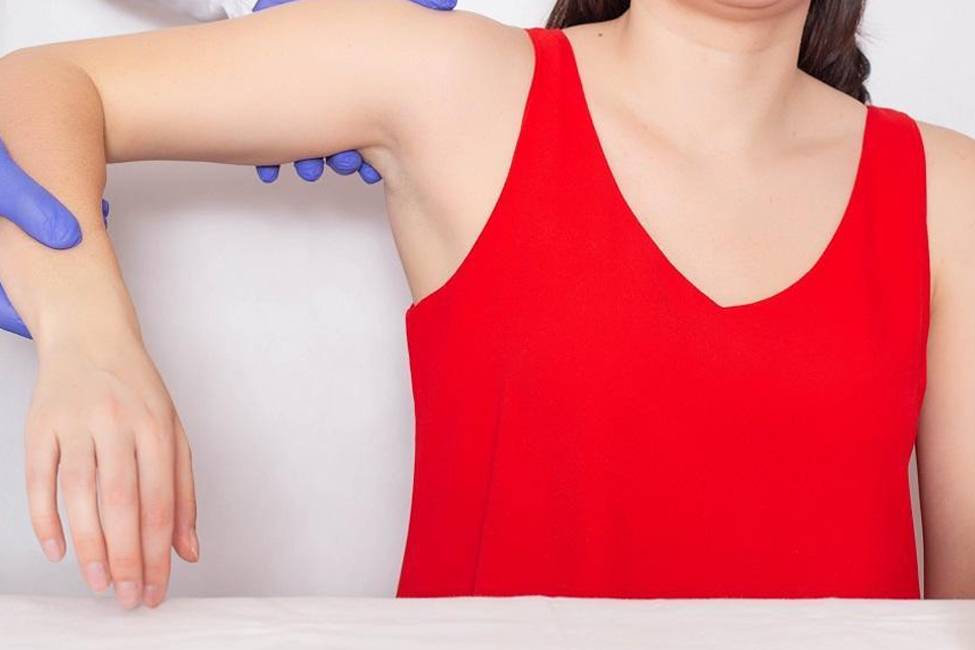
Physical Examination
The doctor will perform a physical examination, assessing your shoulder’s range of motion, strength, and signs of tenderness.
Imaging Tests
X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans may be ordered to visualise the shoulder’s internal structures and confirm the presence and extent of the tear.
Strength and Functional Tests
Specific tests may be conducted to evaluate the shoulder’s strength and functionality and assess the tear’s severity.
Complications of Rotator Cuff Tear
While rotator cuff tears can be managed, if left untreated, they may lead to various complications, including:
- Increased Pain: An untreated tear can cause persistent and potentially worsening shoulder pain.
- Muscle Atrophy: Over time, muscle wasting or atrophy in the affected shoulder may occur, leading to weakness and decreased function.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Without intervention, the tear may result in a significant loss of range of motion in the shoulder joint.
- Inflammation and Tendonitis: The condition can lead to chronic inflammation and associated conditions, such as tendonitis.
- Impact on Daily Activities: Complications can affect your ability to perform everyday tasks, work, or engage in recreational activities.
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tear
Managing a rotator cuff tear can involve several treatment approaches, including:
Conservative Treatment
For smaller tears or less severe cases, conservative treatments may include rest, physical therapy, and pain management to improve symptoms.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections can also help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Physical Therapy
A structured physical therapy program can strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve the range of motion.
Activity Modification
Adjusting daily activities and avoiding actions that worsen symptoms can be part of the treatment plan.
Surgery
Surgical options, such as arthroscopic repair or open surgery, may be recommended for larger tears or when conservative methods are ineffective.
Preventing Rotator Cuff Tears
While you can’t eliminate the risk, there are preventive measures you can take to reduce the likelihood of rotator cuff tears:
- Maintain good posture and use proper techniques when lifting or performing overhead activities to reduce strain on the shoulder.
- When starting new exercise routines or activities, progress slowly to avoid overuse or strain on the shoulder.
- Incorporate shoulder-strengthening exercises into your fitness routine to improve the muscles’ stability around the shoulder joint.
- Ensure adequate rest and recovery between activities to prevent overuse injuries.
- Engage in various exercises and activities to avoid overloading the shoulder with repetitive motions.
- If you experience shoulder pain or discomfort, seek medical attention promptly to address any issues before they progress to a rotator cuff tear.
Living with Rotator Cuff Tear
Living with a rotator cuff tear involves several strategies to manage the condition and maintain shoulder comfort and functionality:
- Adhere to the treatment plan provided by your orthopaedic specialist, which may include physical therapy, pain management, or other therapies.
- Take prescribed medications as directed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Practice the exercises your orthopaedic specialist recommends to strengthen the shoulder and improve mobility.
- Be mindful of activities that may worsen your symptoms, and consider modifications to reduce strain on the shoulder.
- Keep scheduled appointments with your orthopaedic specialist to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Recovery from a rotator cuff tear can be a slow process, and it’s essential to remain patient and persistent in your efforts to improve shoulder function.
A rotator cuff tear is a common and potentially debilitating shoulder injury that can significantly impact daily life. If you suspect a rotator cuff tear, it’s crucial not to promptly ignore your health and seek professional advice. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing this condition effectively.
We encourage you to request an appointment with The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic for expert care and consultation regarding a rotator cuff tear. Our specialised team can provide personalised treatment and guidance, helping you alleviate pain, regain shoulder functionality, and improve your overall quality of life. Don’t hesitate—take the first step toward a healthier, pain-free shoulder by requesting your appointment today.