Ingrown Toenail: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is an Ingrown Toenail?
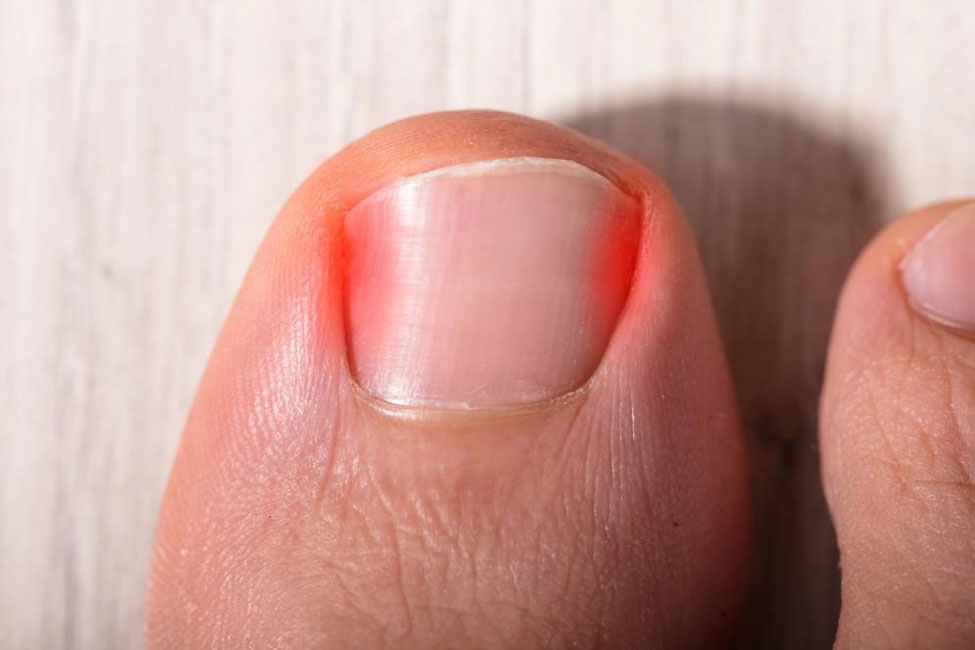
An ingrown toenail is a common foot condition in which the edge of a toenail, usually the big toe, grows into the surrounding skin.
The nail grows into the skin along the edge of the toenail, causing discomfort and potential infection. However, the severity of ingrown toenails can vary from minor discomfort to a more severe, infected condition. Factors such as the depth of the nail into the skin, the presence of infection, and frequency of occurrence may influence the severity.
How Common is Ingrown Toenail?
Ingrown toenails are relatively common, affecting a significant number of individuals. While the exact prevalence may vary, it’s a frequently encountered foot condition seen by podiatrists and professionals. The condition can occur in people of all ages and is often manageable with proper care and treatment.
Causes of Ingrown Toenail
Ingrown toenails can be caused by various factors, including:
- Improper Trimming: Cutting toenails too short or rounding the edges can encourage the nail to grow into the skin.
- Ill-Fitting Footwear: Wearing shoes that are too tight or narrow can exert pressure on the toes, potentially causing toenails to grow into the surrounding skin.
- Foot Trauma: Injury to the toe, either due to repetitive impact or a single event, can lead to ingrown toenails.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing ingrown toenails.
- Abnormal Nail Growth: Irregular or thickened nails can be more prone to becoming ingrown.
Proper foot care and regularly wearing well-fitted shoes can help prevent ingrown toenails.
Symptoms of Ingrown Toenail
Symptoms of an ingrown toenail may include:
- Pain: Discomfort or tenderness along the side of the toenail.
- Redness: The surrounding area might appear red or swollen.
- Inflammation: Swelling around the toenail.
- Infection: Increased pain, warmth, or drainage of pus may indicate an infected ingrown toenail.
- Difficulty Wearing Shoes: Due to the sensitivity and swelling, wearing closed shoes might be uncomfortable.
Severe cases can result in more intense pain or infection.
Diagnosis of Ingrown Toenail
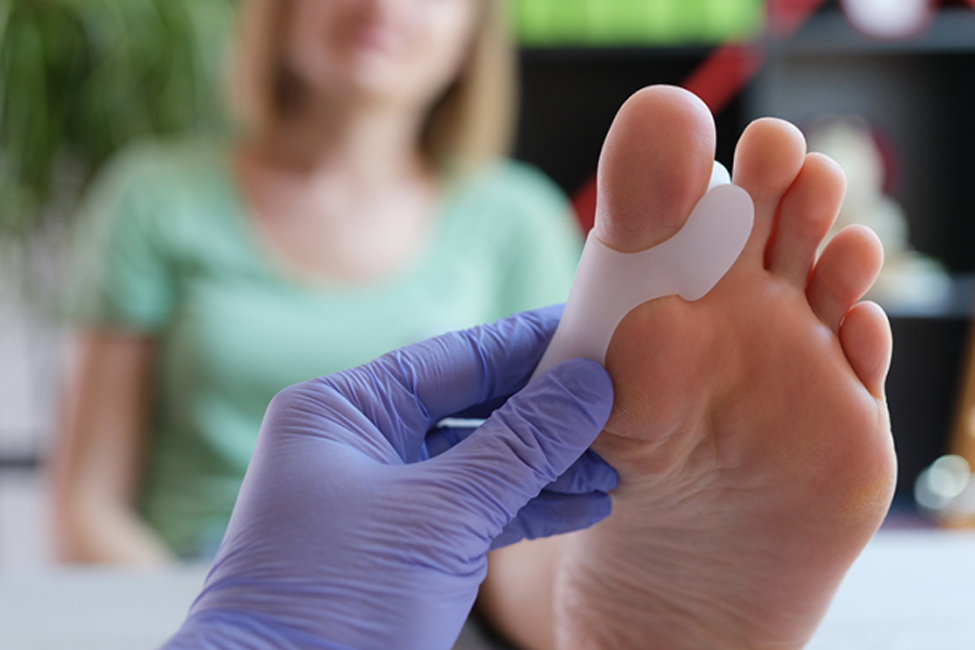
Diagnosing an ingrown toenail typically involves a physical examination by a professional, such as a podiatrist or a doctor. The diagnosis is often made based on the symptoms reported by the individual and the visible signs of the ingrown toenail, including redness, swelling, and tenderness.
In some cases, the healthcare provider might gently push on the skin around the toenail to assess tenderness and determine the best course of treatment. If the area is infected, they may recommend additional tests or procedures to manage it.
Complications of Ingrown Toenail
Complications related to an ingrown toenail can include:
- Infection: If an ingrown toenail breaks the skin or causes an open wound, bacteria can enter, leading to an infection. This can cause increased pain, warmth, redness, and drainage of pus.
- Cellulitis: If the infection worsens, it can spread to the surrounding skin, causing redness, warmth, and tenderness over a larger area.
- Abscess Formation: In severe cases, pus (abscess) can develop in the skin next to the nail.
- Chronic Pain: Repeated ingrown toenails or untreated cases can result in chronic pain and discomfort.
Treatment Options for Ingrown Toenail
Treatment options for an ingrown toenail may include:
Soaking
Soaking the affected foot in warm, soapy water several times a day can reduce swelling and tenderness.
Proper Trimming
Gently lift the edge of the ingrown nail and place a small piece of cotton or dental floss under it to encourage the nail to grow over the skin rather than into it
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort.
Antibiotics
If an infection is present, oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
Surgical Intervention
For severe cases or recurring ingrown toenails, a professional might perform a minor surgical procedure to remove a portion of the affected nail and prevent it from growing into the skin.
Preventing Ingrown Toenail
To prevent ingrown toenails, consider the following tips:
- Cut nails straight across and avoid rounding the edges. Trim them to the edge of the toe, but not too short.
- Select shoes that provide enough room for your toes and don’t squeeze them. Avoid shoes with narrow or tight toe boxes.
- Keep your feet clean and dry to prevent infection. Wear clean socks and change them regularly.
- If your feet are at risk of injury (for instance, during athletic activities), consider wearing protective footwear to prevent toe trauma.
- Check your feet regularly for any signs of an ingrown toenail, especially if you have a history of it.
Living with Ingrown Toenail
Living with an ingrown toenail can be uncomfortable, but following certain practices can help manage the condition:
- Practice proper foot hygiene, keeping the affected toe clean and dry.
- Try to avoid tight-fitting footwear or socks that put pressure on the toes.
- Over-the-counter pain medications can help alleviate discomfort. Soaking the foot in warm water can also reduce pain and swelling.
- Refrain from attempting to trim or treat an ingrown toenail yourself, especially if it’s causing pain or shows signs of infection. Seek professional medical advice.
- If there’s an infection, increased pain, or if the ingrown toenail becomes severe or recurrent, seek professional help. Don’t ignore persistent or worsening symptoms.
Ingrown toenails can cause discomfort and potential complications if not addressed properly. It’s essential to manage them promptly and effectively. Address any discomfort or signs of an ingrown toenail early to prevent further complications.
Follow proper foot hygiene practices, such as trimming nails correctly and wearing comfortable footwear to reduce the risk of an ingrown toenail. Seek guidance from a professional to determine the most suitable treatment and avoid self-treatment that might worsen the condition.
If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort or suspect an ingrown toenail, we strongly recommend scheduling an appointment with The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic for expert assessment and suitable care.
Seeking timely professional care is crucial for managing ingrown toenails and preventing potential complications.