Paediatric Flat Feet: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is Paediatric Flat Feet?
Paediatric flat feet, also known as pediatric or children’s flat feet, is a condition in which a child has little to no arch in the sole of their foot. It is a common and typically painless condition in children where the arches do not develop as expected, resulting in the entire sole making contact with the ground when standing.
Type of Paediatric Flat Feet
There are two main types of paediatric flat feet:
- Flexible Flat Feet: In this type, the arch is present when the child sits or stands on their tiptoes but disappears when they put weight on their feet.
- Rigid Flat Feet: The arch is absent when the child is sitting and when they stand, and the feet remain flat regardless of weight-bearing.
How Common is Paediatric Flat Feet?
Paediatric flat feet are relatively common, especially in infants and young children. As children grow, many will naturally develop arches in their feet. It is a normal developmental variation; most children with flat feet do not experience pain or require treatment.
Causes of Paediatric Flat Feet
Paediatric flat feet can result from various factors, including:
- Genetics: Family history can play a role in children’s development of flat feet.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles that support the arch of the foot can contribute to flat feet.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Some children with conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome may be more prone to flat feet.
- Injury or Trauma: A foot injury or trauma can affect the development of arches in children.
- Neurological Conditions: Certain neurological conditions can influence foot alignment and arch development.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put extra stress on the feet and contribute to flat feet.
Symptoms of Paediatric Flat Feet
Children with flat feet may not always exhibit symptoms, but when present, the following signs can be observed:
- Pain: Some children may experience pain in the feet, particularly around the arch area or the inside of the ankle.
- Tired or Aching Feet: After physical activity or prolonged periods of standing, a child may complain of tired or aching feet.
- Difficulty with Footwear: Finding comfortable shoes may be challenging due to the need for arch support.
- Toe Abnormalities: Flat feet, such as hammertoes, can sometimes contribute to toe abnormalities.
- Reduced Mobility: A child may have limitations in activities that require running, jumping, or physical agility.
Diagnosis of Paediatric Flat Feet
Diagnosing paediatric flat feet typically involves the following steps:
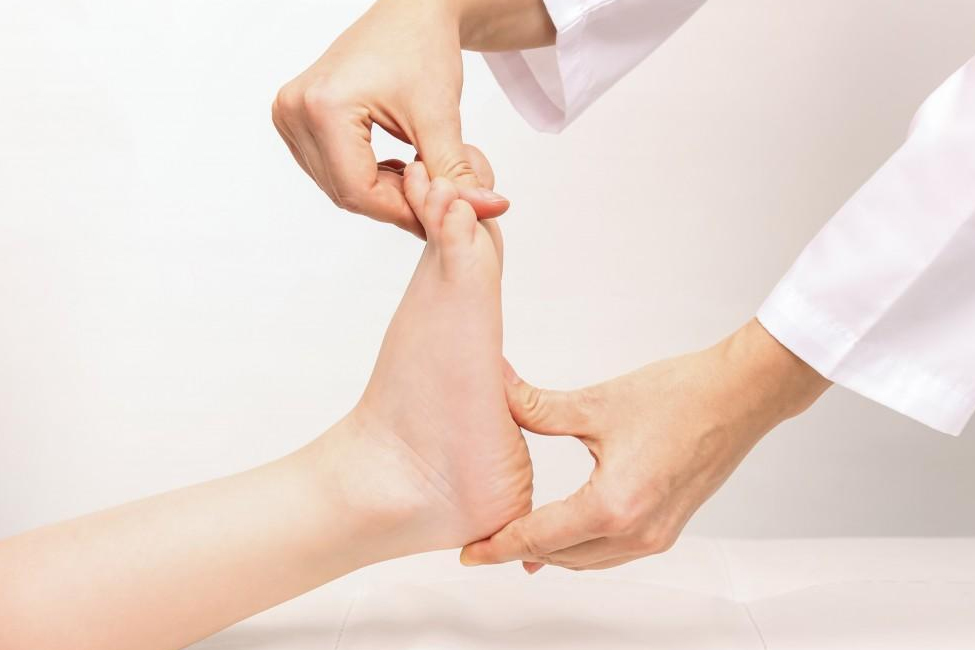
Clinical Examination
An orthopaedic specialist will conduct a physical examination, assessing the child’s feet while sitting, standing, and during various movements.
Family History
Information about family history may be gathered to understand if there’s a genetic predisposition to flat feet.
Assessment of Symptoms
If the child experiences pain or discomfort, the provider will inquire about the symptoms’ location, frequency, and duration.
Gait Analysis
Observing the child’s gait (how they walk) can provide valuable insights into any biomechanical issues related to the flat feet.
Imaging
In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays may be ordered to assess the bones and alignment of the feet.
Complications of Paediatric Flat Feet
While paediatric flat feet are often a normal variation of foot development and do not necessarily lead to complications, in some cases, they can contribute to the following issues:
- Foot Pain: Children with flat feet may experience pain, particularly after physical activity.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Discomfort or pain can limit a child’s participation in sports and physical activities.
- Joint Problems: In some cases, flat feet can lead to misalignment of the leg joints, potentially causing knee or hip pain.
- Shoe Fit Issues: Finding appropriate footwear with arch support can be challenging for children with flat feet.
- Developmental Delays: Severe flat feet in rare cases may be associated with developmental delays, but this is not common.
Treatment Options for Paediatric Flat Feet
The management of paediatric flat feet may involve several approaches, including:
Observation
In many cases, no treatment is necessary, and the orthopaedic specialist may recommend periodic monitoring as many children naturally outgrow flat feet.
Footwear
Supportive and well-fitted shoes with arch support can benefit children with flat feet. Custom orthotic insoles may also help.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles and improve foot and ankle stability.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises can improve calf muscles and Achilles tendon flexibility, which may alleviate symptoms.
Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended to manage pain or discomfort.
Surgery (Rarely)
Surgical intervention may be considered in severe cases with significant symptoms or structural abnormalities, but this is rare.
Preventing Paediatric Flat Feet
While paediatric flat feet are often a normal part of development, you can take steps to promote healthy foot development and potentially reduce the risk:
- Ensure your child wears well-fitted, supportive shoes with arch support, especially during physical activities.
- Regular physical activity and exercises that promote foot and leg strength and flexibility can be beneficial.
- Teach your child good foot care habits, such as keeping feet clean and dry, trimming toenails properly, and wearing appropriate footwear.
- Schedule regular checkups with an orthopaedic specialist to monitor foot development and address any concerns early.
- Encourage a balanced diet to maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can stress the feet.
- If there’s a family history of flat feet or related issues, discuss this with your orthopaedic specialist for early assessment.
Living with Paediatric Flat Feet
Living with paediatric flat feet generally involves these key points:
- Regularly visit an orthopaedic specialist to monitor your child’s foot development and discuss any concerns or symptoms.
- Ensure your child wears well-fitted shoes with arch support, especially during physical activities, to alleviate discomfort.
- Encourage your child to engage in regular physical activity and exercises that promote foot and leg strength and flexibility.
- If your child experiences pain or discomfort, discuss pain management options with an orthopaedic specialist to maintain their quality of life.
- If necessary, adhere to your orthopaedic specialist’s recommendations regarding treatment, exercises, and lifestyle modifications.
Paediatric flat feet are a common and often benign condition in children. While many kids naturally outgrow flat feet, it’s important to monitor your child’s foot development and address any symptoms or concerns.
If you have questions or your child experiences pain, discomfort, or mobility issues related to flat feet, we encourage you to seek professional advice. We recommend requesting an appointment with The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic for expert care and consultation regarding paediatric flat feet. Our specialised team can provide guidance, evaluation, and treatment options, ensuring your child’s foot health and overall well-being. Don’t hesitate—take the first step towards your child’s healthy and pain-free feet by requesting an appointment today.