Golfer’s Elbow: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is a Golfer’s Elbow?
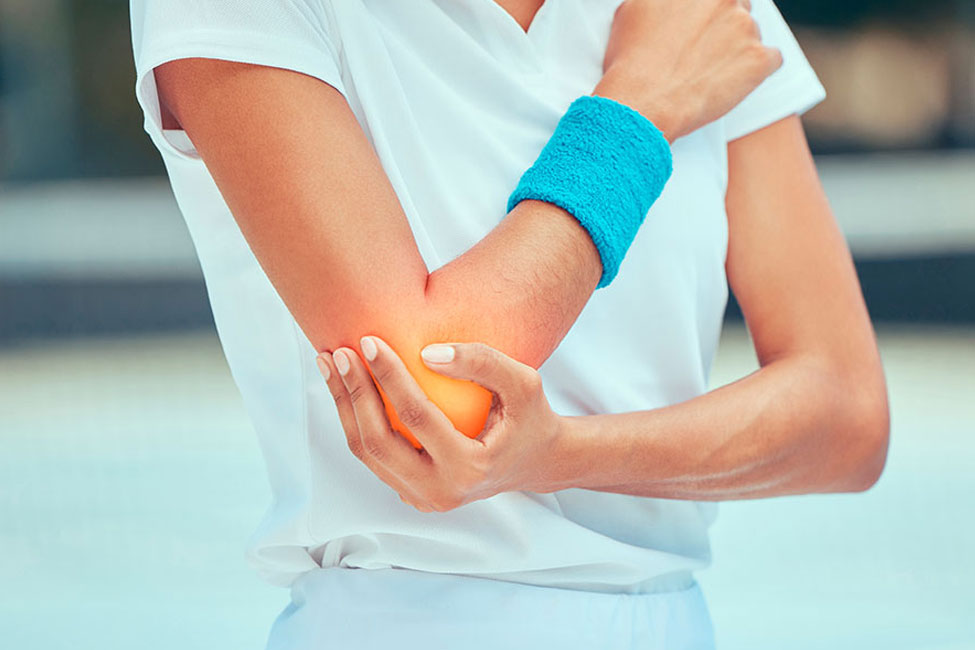
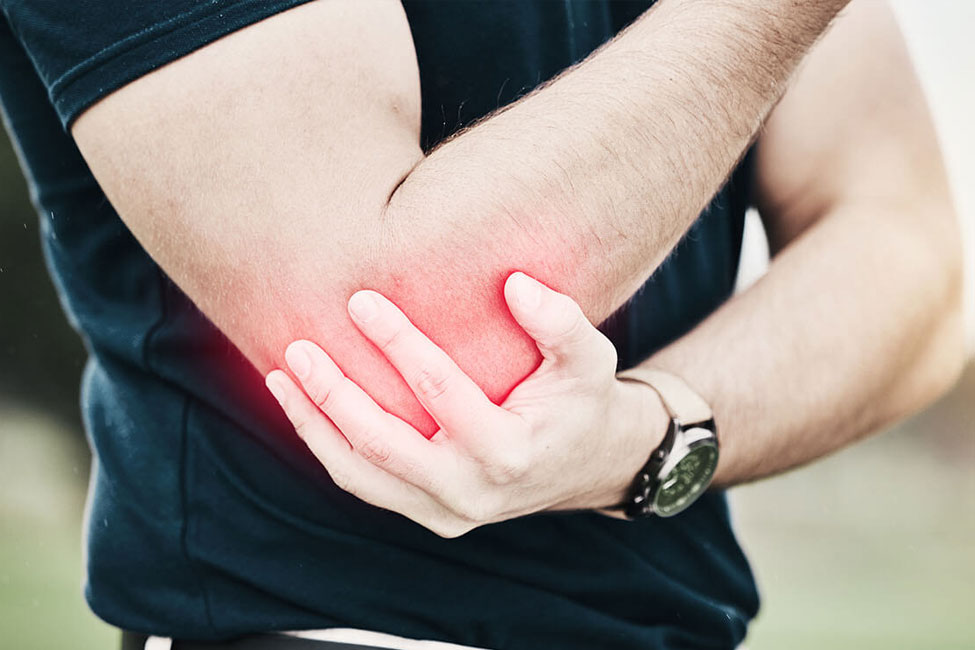
Golfer’s Elbow, known medically as medial epicondylitis, is a condition causing pain and inflammation on the inner side of the elbow. Despite its name, it’s not exclusive to golfers and can affect anyone who repeatedly uses their wrists or clenches their fingers, leading to overuse or strain on the tendons.
While it commonly affects the flexor tendons of the forearm, it can specifically impact the tendon known as the common flexor tendon or the pronator teres tendon. This overuse can lead to pain and inflammation in the tendons connected to the bony bump on the inner side of the elbow, known as the medial epicondyle.
How Common is Golfer’s Elbow?
Golfer’s Elbow is a relatively common condition. It can affect a wide range of individuals, from athletes engaging in repetitive wrist or forearm movements (such as golfers, hence the name), to non-athletes involved in tasks that strain the tendons on the inner side of the elbow. While its prevalence may vary, it is a frequently encountered overuse injury among individuals who repetitively stress the flexor tendons in the forearm
Causes of Golfer’s Elbow
Golfer’s Elbow, or medial epicondylitis, is primarily caused by repetitive or forceful use of the forearm muscles. The repetitive movements lead to overuse and strain on the tendons that attach to the inner part of the elbow. Common causes include:
- Repetitive Movements: Activities requiring repetitive wrist flexion, such as swinging a golf club, can strain the tendons.
- Gripping Activities: Grasping or gripping objects for extended periods, common in golf, weightlifting, or carpentry, can contribute to the condition.
- Improper Technique: Using a poor form or incorrect equipment during physical activities can increase the risk of a Golfer’s Elbow.
- Sudden Forceful Movements: An acute injury or sudden excessive force can strain the tendons, leading to a Golfer’s Elbow.
Symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow
Symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow, or medial epicondylitis, typically include:
- Pain: Often felt on the inner side of the elbow. It might radiate down the forearm.
- Weakness: Difficulty gripping or lifting objects due to the affected tendon.
- Stiffness: The elbow may feel stiff, limiting movement.
- Tenderness: The inner side of the elbow might be tender to the touch.
- Numbness or Tingling: Some individuals might experience sensations like numbness or tingling in the fingers.
These symptoms often develop gradually over time, especially with repetitive use or strain on the forearm tendons, and can affect daily activities.
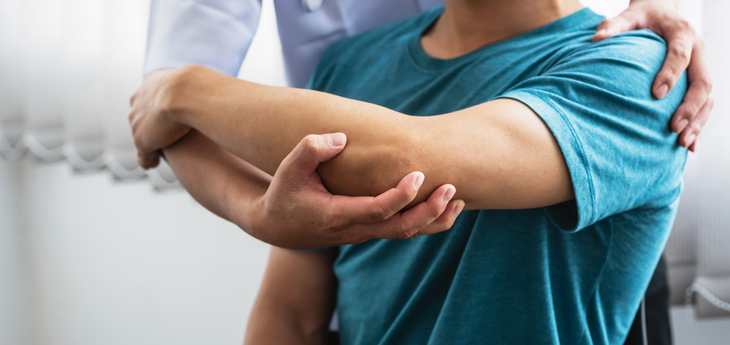
Diagnosis of Golfer’s Elbow
Diagnosing Golfer’s Elbow typically involves a comprehensive assessment by a professional, which may include:
Medical History
The doctor will discuss the symptoms and examine the elbow to understand the extent of pain, tenderness, and limitation of movement.
Physical Examination
This involves checking for pain and tenderness around the affected area, as well as assessing the range of motion and strength.
Imaging Tests
X-rays or other imaging studies might be ordered to rule out other potential causes or to evaluate the severity of the condition. In some cases, an MRI might be recommended to assess soft tissues for tendon damage.
Complications of Golfer’s Elbow
Complications from the Golfer’s Elbow are typically not severe but can affect daily activities and the affected arm. Some possible complications include:
- Chronic Pain: If left untreated or aggravated by repetitive strain, Golfer’s Elbow can lead to persistent discomfort and chronic pain in the elbow and forearm.
- Reduced Functionality: The condition might limit the range of motion in the affected arm, reducing its strength and flexibility.
- Difficulty in Activities: Simple tasks that involve gripping, lifting, or bending the elbow may become challenging due to pain and weakness.
- Impact on Performance: Athletes or individuals engaged in activities requiring repetitive arm movement might experience limitations in their performance due to the discomfort.
Treatment Options for Golfer’s Elbow
Treatment for Golfer’s Elbow, or medial epicondylitis, often includes a combination of conservative measures. These can include:
Rest
Avoiding or modifying activities that aggravate the condition to allow the tendons to heal.
Ice Application
Applying ice to the affected area several times a day can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy
Specific exercises can help strengthen and stretch the affected muscles and tendons.
Bracing or Splinting
Wearing a brace or forearm strap can reduce strain on the affected tendons.
Preventing Golfer’s Elbow
To help prevent Golfer’s Elbow or reduce the risk of its recurrence, consider the following preventive measures:
- Ensure proper form and equipment when engaging in sports or physical activities to avoid unnecessary strain on the tendons.
- Gradually increase the intensity or duration of activities to allow the tendons to adapt and reduce the risk of overuse.
- Before physical activities, warm-up exercises and stretching routines can prepare the muscles and tendons, reducing the likelihood of strain.
- Incorporate exercises to strengthen the forearm and wrist muscles to support the tendons and prevent injuries.
- Using the right equipment that fits properly and is suitable for the activity can prevent undue stress on the tendons.
- Allow adequate rest between activities and listen to your body to prevent overuse and give the tendons time to recover.
Living with a Golfer’s Elbow
Living with a Golfer’s Elbow might involve adjusting activities and lifestyle to manage and alleviate symptoms. Consider the following tips for living with Golfer’s Elbow:
- Avoid or modify activities that trigger pain, and practice techniques that minimise stress on the affected tendons.
- Use ice packs or cold compresses to reduce inflammation, and consider taking breaks or resting the affected arm as needed.
- Use prescribed exercises or physical therapy routines to strengthen and stretch the forearm muscles and tendons.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort, and following a doctor’s advice on medication can be beneficial.
- Use proper ergonomics and techniques during daily activities to reduce strain on the elbow and forearm.
- A brace or forearm strap might support the area and reduce strain on the tendons during activities.
- Regularly follow up with professionals to monitor progress, modify treatment if necessary, and prevent the condition from worsening.
Golfer’s Elbow can significantly impact daily activities, causing discomfort and limitations in arm movement. However, there are numerous management strategies available to alleviate symptoms and prevent their recurrence.
If you’re experiencing persistent elbow pain or suspect Golfer’s Elbow, it’s crucial to seek professional advice. Our team at The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic is here to help. Don’t let discomfort hinder your activities. Contact us today for an appointment and personalised care.
Remember, early intervention and proper management are key to a smoother recovery from Golfer’s Elbow.