Flat Foot: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is a Flat Foot?
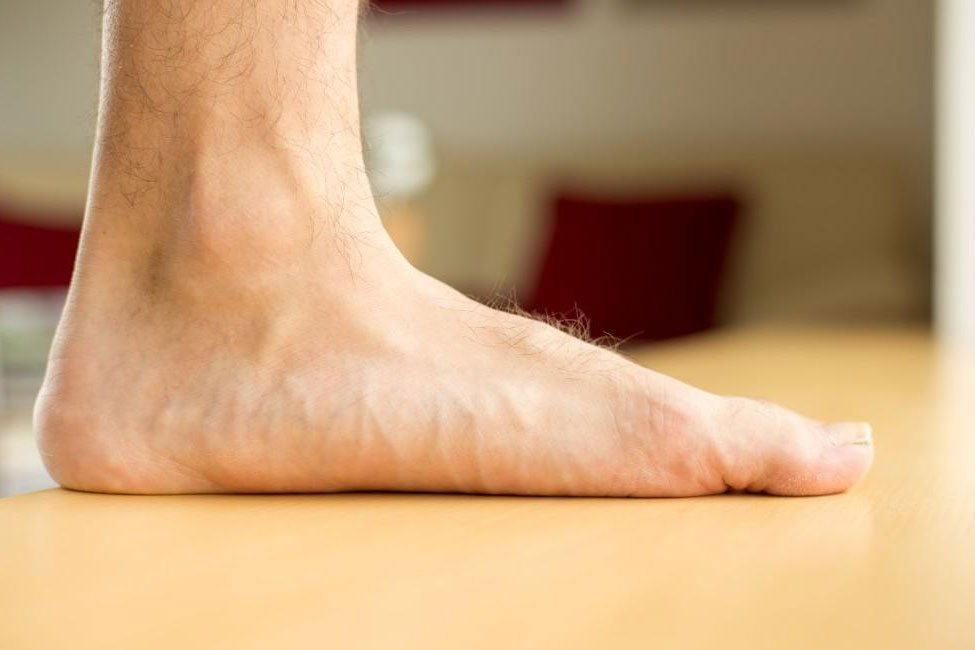
Flat foot, also known as pes planus, is a condition where the arches of the feet collapse or have a very low arch, making the entire sole come into contact with the ground when standing. It can be present from childhood or can develop later in life.
Type of Flat Foot
Types of flat feet can be categorised as flexible flat feet and rigid flat feet:
- Flexible Flat Feet: This type appears when standing but disappears when the person elevates their foot, as the arch becomes visible. It’s often painless and doesn’t typically cause major issues.
- Rigid Flat Feet: In this type, the arch remains flat even when the foot is elevated. It tends to be less common but may lead to more severe symptoms and discomfort.
How Common is Flat Foot?
Flat feet are relatively common and can be seen in both children and adults. It’s estimated that approximately 20-30% of the population have flat feet. Some individuals may experience no symptoms or issues due to their flat feet, while others might face pain or discomfort, particularly if the condition affects their gait or causes strain on other parts of the body, like the ankles or knees.
Causes of Flat Foot
Flat foot can develop due to various factors:
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit flat feet from their family members, as the condition can run in families.
- Abnormal Foot Development: Issues during the growth and development of the foot, such as abnormal positioning of bones or joints, can lead to flat feet.
- Injuries or Conditions: Foot or ankle injuries, arthritis, nerve conditions, or muscle diseases can contribute to the development of flat feet.
- Overpronation: Overpronation occurs when the feet roll inward excessively while walking, leading to the arches collapsing and causing flat feet.
- Obesity: Excessive weight can put added pressure on the feet, potentially contributing to the development of flat feet.
- Pregnancy: Flat feet can sometimes develop or worsen during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect the ligaments in the body.
Symptoms of Flat Foot
Symptoms associated with flat feet can vary from person to person. While some individuals might have flat feet without experiencing any discomfort or issues, others may have symptoms such as:
- Pain: Discomfort can occur in the arch, heel, ankle, or along the inner side of the foot.
- Swelling: Some individuals might notice swelling along the inside of the ankle.
- Difficulty in Foot Movement: Flat feet can sometimes cause limitations in foot movement, leading to challenges with running or walking.
- Foot Fatigue: The feet may tire easily or feel fatigued due to the lack of arch support.
- Lower Leg Pain: Pain or discomfort may extend from the feet into the lower legs.
- Misalignment in the Legs: Flat feet can lead to misalignment in the lower limbs, causing issues in the knees or hips.
Diagnosis of Flat Foot
Diagnosing flat feet typically involves a combination of a physical examination and, if needed, imaging tests. A healthcare professional, usually a podiatrist or orthopaedic specialist, will typically:
Physical Examination
The doctor will observe the feet while standing and sitting, checking for visible signs of a lowered or absent arch. They may also evaluate how the feet and ankles move and how the individual walks.
Gait Analysis
This involves observing the individual’s gait or walking pattern to assess any abnormalities or issues in movement that may be related to flat feet.
Imaging Tests
X-rays may be used to examine the structure of the foot and ankle bones to detect any misalignments or structural abnormalities.
Complications of Flat Foot
Flat feet, in some cases, may lead to certain complications or issues. These can include:
- Foot Pain: Discomfort or pain in the feet, especially after extended periods of standing or physical activity.
- Misalignment in the Lower Limbs: Flat feet may cause overpronation, leading to misalignment in the lower limbs and potentially causing issues in the ankles, knees, or hips.
- Joint Problems: Flat feet can contribute to joint problems and arthritis due to the increased stress on the joints of the feet and lower limbs.
- Foot Fatigue: Due to the lack of arch support, individuals with flat feet might experience fatigue or discomfort in their feet more quickly than those with normal arches.
- Back Pain: Misalignment in the lower limbs might lead to posture issues and result in back pain for some individuals.
Treatment Options for Flat Foot
Treatment for flat feet depends on the severity of symptoms and the impact on an individual’s daily life. Here are some common approaches:
Orthotic Devices
Custom-made or over-the-counter shoe inserts, arch supports, or orthotic devices can provide additional arch support and alleviate discomfort.
Supportive Footwear
Shoes with proper arch support and adequate stability can help reduce discomfort associated with flat feet.
Physical Therapy
Specific exercises and stretches can help strengthen muscles and improve foot function.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the feet and lower limbs.
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can alleviate pain or inflammation.
Surgery (in Severe Cases)
In rare instances when flat feet cause severe pain or discomfort that doesn’t respond to conservative treatments, surgery might be considered to correct structural issues in the feet.
Preventing Flat Foot
While some causes of flat feet, like genetics, cannot be prevented, some steps may help reduce the risk of developing or worsening the condition:
- Excess weight can increase pressure on the feet and contribute to the development or exacerbation of flat feet.
- Wear shoes that provide adequate arch support and cushioning, especially during activities that involve prolonged standing or walking.
- When possible, avoid walking barefoot, especially on hard surfaces. Supportive footwear helps provide necessary support for the feet.
- Engage in exercises that strengthen the muscles in the feet and lower limbs to provide better support for the arches.
- Regularly inspect your feet for any changes, pain, or discomfort. If you notice any issues, seek medical advice.
Living with Flat Foot
Living with flat feet often involves managing symptoms and making lifestyle adjustments to reduce discomfort. Here are some tips:
- Opt for shoes with good arch support and cushioning to alleviate discomfort associated with flat feet.
- Consider using custom-made or over-the-counter shoe inserts or orthotic devices to provide additional support.
- Perform exercises and stretches recommended by a healthcare professional to strengthen foot muscles and improve foot function.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the feet and lower limbs.
- Schedule periodic check-ups with a podiatrist or orthopaedic specialist to monitor foot health and address any changes or discomfort.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers, as recommended, to manage discomfort or inflammation.
Flat feet can be a common condition, and while it might not always cause significant issues, for some, it can lead to discomfort or affect daily activities. Managing flat feet involves appropriate care, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, seeking professional guidance. If you’re experiencing discomfort or limitations due to flat feet, don’t hesitate to seek expert advice.
For personalised evaluation and guidance, we encourage you to request an appointment with The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic. Our specialists can provide tailored recommendations and support to manage flat feet and improve foot health and overall well-being. Your comfort and health matter to us. Contact us today for expert care.