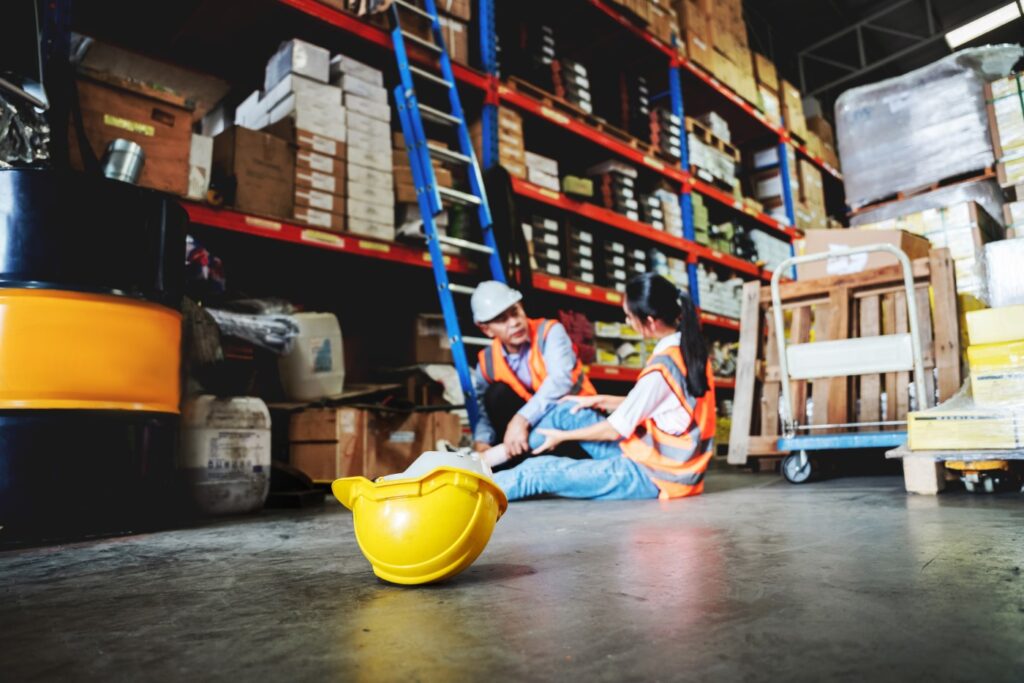
In work environments, especially those involving physical labour, the risk of stress fractures, particularly in the foot and ankle, is quite a concern. These tiny cracks in the bone can develop from repetitive force or overuse, often unnoticed until the pain worsens. However, adjusting to physical tasks and taking preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of stress fractures, promoting better orthopaedic health.
What Are Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are small cracks in the bone that occur due to repetitive stress and overuse. Unlike acute fractures caused by a single high energy injury, stress fractures result from cumulative low energy strain. This is particularly common in workplaces involving standing for long periods, walking, lifting, or repetitive movements.
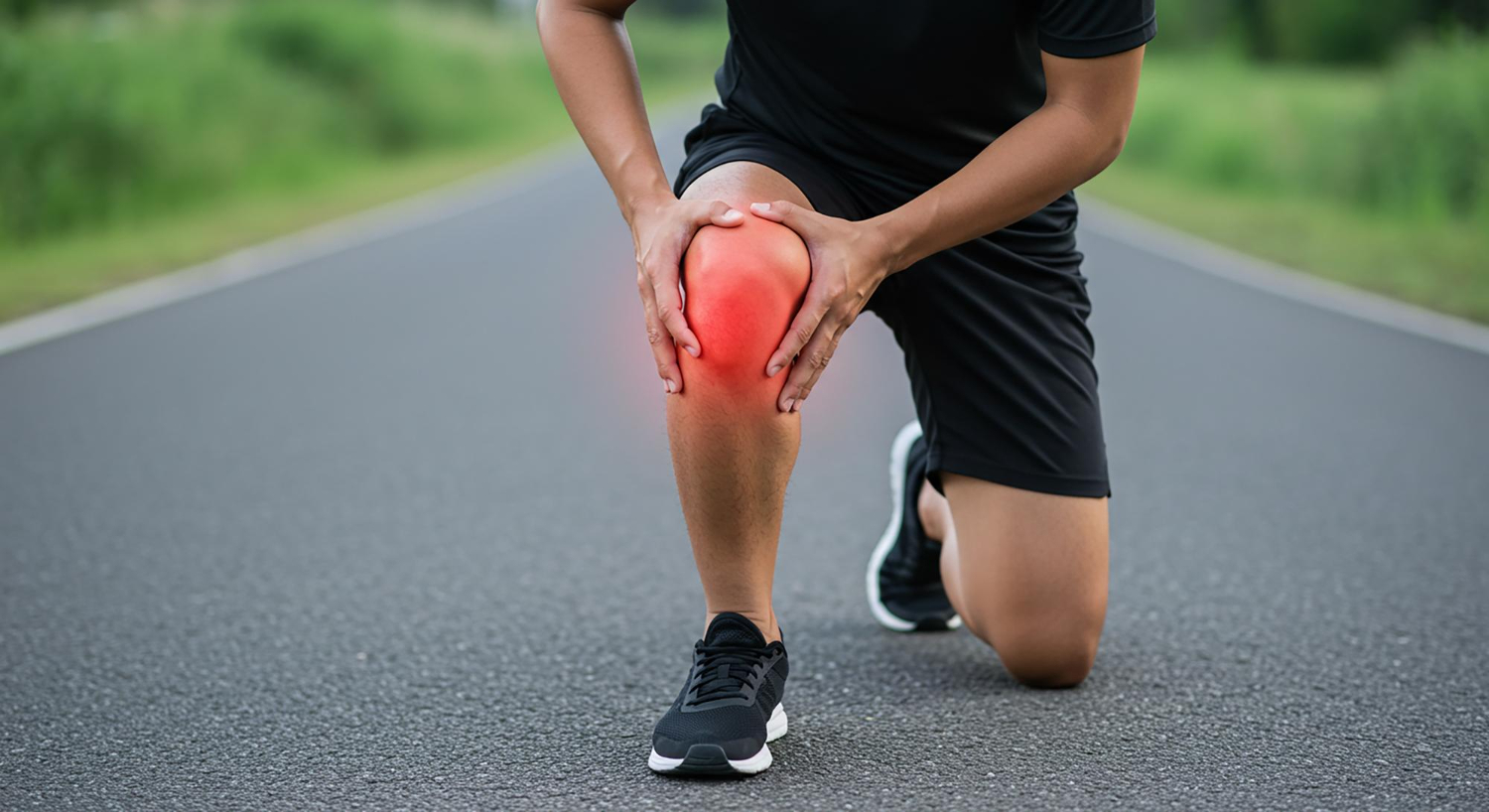
The feet and ankles bear the brunt of our weight and are essential for movement. The bones can develop micro-damage when these parts are subjected to continuous stress without adequate rest or support. Common symptoms include pain and swelling that worsens with activity and improves with rest and elevation.
Why Do You Need To Keep Your Ankle and Feet Healthy?
Our feet and ankles are complex structures comprising bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. They provide stability, balance, and mobility. If not properly addressed, stress fractures in these areas can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and long-term complications. Therefore, modifying physical tasks to prevent such injuries is important for both short-term and long-term health.
Practical Tips to Modify Physical Tasks
1. Ergonomic Assessment and Adjustments
Conduct an ergonomic workplace assessment to identify tasks that might contribute to stress fractures. Adjust workstations and processes to minimise repetitive strain on the feet and ankles. For example, make sure that work surfaces are at an appropriate height to prevent awkward postures and excessive reaching.
2. Footwear Matters
Invest in high-quality, supportive footwear. Shoes should have adequate cushioning, arch support, and fit well. For those working on hard surfaces, consider shock-absorbing insoles. Rotating between different pairs of shoes can also help reduce repetitive strain.
3. Surface Modifications
If the workplace has hard flooring, consider installing anti-fatigue mats. These mats can reduce the impact on feet and ankles, especially for workers who stand for prolonged periods. Additionally, encourage workers to shift their weight and change positions regularly to avoid constant pressure on specific areas.
4. Task Rotation and Breaks
Implement a task rotation schedule to make sure that employees are not performing the same activities for extended periods. This reduces the repetitive stress on any one part of the body. Regular breaks are equally important, allowing muscles and bones time to recover.
5. Strengthening and Conditioning Exercises
Encourage employees to engage in exercises that strengthen the muscles around the feet and ankles. Stronger muscles provide better support and reduce the risk of stress fractures. Simple exercises like calf raises, toe curls, and ankle rotations can be effective.
6. Proper Lifting Techniques
Train employees on proper lifting techniques to avoid placing undue stress on the lower extremities. Lifting with the legs rather than the back and avoiding twisting movements can prevent unnecessary strain on the ankles and feet.
7. Gradual Increase in Activity Levels
For employees who are new to physically demanding tasks, make sure that there’s a gradual increase in activity levels. Sudden spikes in physical activity can overwhelm the bones and muscles, increasing the risk of stress fractures.
8. Hydration and Nutrition
Promote proper hydration, nutrition and adequate sun exposure. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake are crucial for bone health. Encourage employees to stay hydrated, as dehydration can lead to muscle fatigue and increase the risk of injuries.
Workplace Culture and Support
Creating a supportive workplace culture is essential for implementing these changes effectively. Management should emphasise the importance of orthopaedic health and provide the necessary resources and training. Employees should feel comfortable reporting discomfort or early symptoms of stress fractures without fear of repercussions.
Early Detection and Response
Early detection of stress fractures can prevent them from worsening. Encourage employees to report any persistent pain or discomfort in their feet or ankles. Providing access to medical evaluations and appropriate interventions can make a significant difference.
Preventing stress fractures in the workplace, particularly in the feet and ankles, is crucial for maintaining a healthy, productive workforce. By making ergonomic adjustments, promoting proper footwear, implementing task rotation, and encouraging strengthening exercises, workplaces can significantly reduce the risk of these injuries. Fostering a supportive environment where employees feel empowered to take care of their orthopaedic health will lead to better outcomes for everyone. Remember, a little preventative care today can save a lot of pain and trouble tomorrow.