Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects the hand and wrist. It occurs when the median nerve runs from the forearm into the hand and becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. This can result in pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hand and fingers. CTS is a common condition caused by various factors, including repetitive hand movements and underlying health conditions.
Type of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be classified into two main types:
- Idiopathic CTS: This is the most common type and often has no specific known cause.
- Secondary CTS: This type is associated with underlying conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or pregnancy, which can increase the risk of CTS.
How Common is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a relatively common condition, with millions of cases reported each year. It is especially prevalent among people who engage in repetitive hand or wrist movements, such as those who work on computers or perform manual labour. The condition’s prevalence varies by age, occupation, and other factors, making it a significant concern in orthopaedics and hand health.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can develop due to several causes, including:
- Repetitive Hand Use: Repetitive hand or wrist movements, such as typing, vibrating tools, or assembly line work, can irritate the median nerve over time.
- Anatomy: Some individuals have a narrower carpal tunnel, which can increase the risk of compression on the median nerve.
- Health Conditions: Underlying health issues, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disorders, can lead to CTS.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and fluid retention during pregnancy can increase pressure on the median nerve.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to increased pressure on the carpal tunnel, potentially causing CTS.
- Trauma or Injury: A wrist injury or trauma can lead to swelling and compression of the median nerve.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
If you have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), you may experience the following symptoms:
- Hand Numbness: You might feel numbness or a “pins and needles” sensation in your hand, especially in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
- Hand Weakness: Weakness in the hand can make it challenging to grip or hold objects.
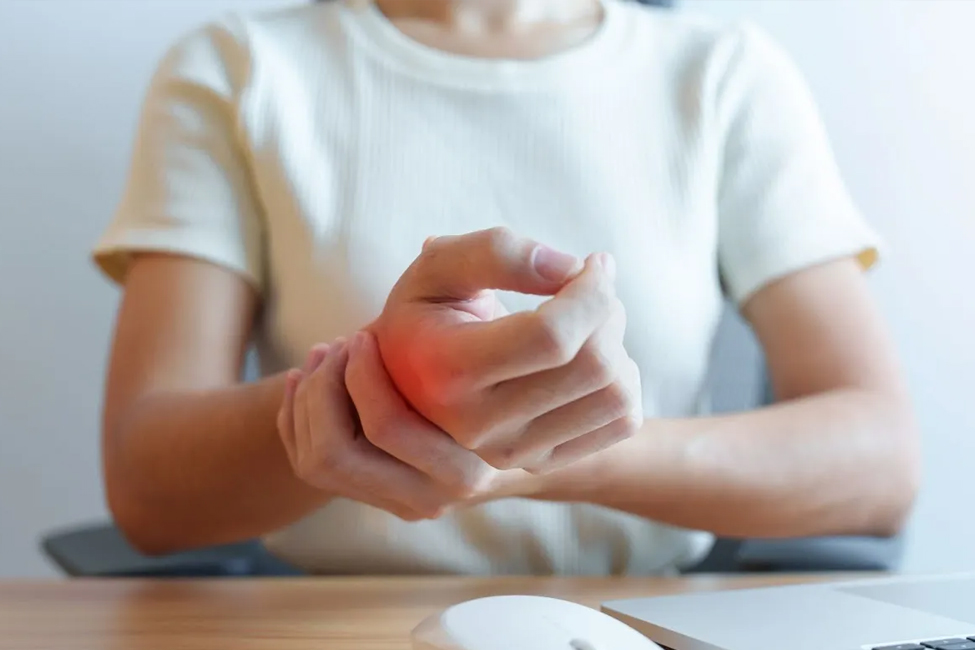
- Pain or Discomfort: You may experience pain or discomfort in the hand or wrist, which can sometimes extend up the arm.
- Tingling Sensation: Like electric shocks, a tingling sensation may be felt in the affected hand and fingers.
- Nighttime Symptoms: Symptoms often worsen at night, causing sleep disturbances.
- Difficulty with Fine Motor Skills: You might find it challenging to perform tasks that require fine motor skills, like buttoning a shirt.
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
To diagnose Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), orthopaedic specialists typically follow these steps:
Medical History
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, including when they started and any factors that worsen or alleviate them.
Physical Examination
The doctor will examine your hand, wrist, and arm to check for signs of CTS, including muscle strength, sensation, and reflexes.
Tinel's Test
This test involves lightly tapping over the median nerve to check for any tingling or electric shock-like sensations, which can be a sign of CTS.
Phalen's Test
This test involves bending your wrist to a 90-degree angle to see if it triggers symptoms.
Nerve Conduction Studies
These tests measure the speed of electrical signals along your nerves and can help confirm CTS.
Electromyography (EMG)
EMG measures the electrical activity in muscles and can help diagnose nerve-related conditions.
Complications of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) can lead to various complications if left untreated, including:
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain in the hand and wrist can significantly impact daily activities and reduce your quality of life.
- Muscle Atrophy: Over time, untreated CTS can lead to muscle weakness and atrophy in the affected hand.
- Reduced Dexterity: Hand weakness and numbness can reduce dexterity, making performing fine motor skills and tasks challenging.
- Sleep Disturbances: CTS symptoms often worsen at night, leading to sleep disturbances and fatigue.
- Functional Limitations: The condition can limit your ability to perform everyday activities and tasks that require using your hands.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
When dealing with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), your orthopaedic specialist may recommend these treatment options:
Wrist Splinting
Wearing a wrist splint, especially at night, can help keep your wrist in a neutral position and reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroid Injections
Your doctor may administer corticosteroid injections into the carpal tunnel to reduce swelling and alleviate symptoms.
Physical Therapy
Engaging in physical therapy can help improve hand strength and flexibility.
Lifestyle and Activity Modifications
Changing hand and wrist movements and ergonomics can reduce strain and alleviate symptoms.
Surgery
Surgery to release the carpal tunnel may be recommended in more severe cases or when conservative treatments are ineffective.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
To reduce the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), consider these preventive measures:
- Maintain proper hand and wrist ergonomics during repetitive hand movements, like typing or assembly work.
- Take regular breaks to rest your hands and perform stretching exercises during repetitive tasks.
- Consider using ergonomic tools and wrist supports to minimise strain on your wrists.
- Practice hand and wrist exercises to improve flexibility and strength.
- Learn and use correct typing techniques to minimise strain on your wrists.
- Managing your weight can reduce the risk of CTS, as excess weight can pressure the carpal tunnel.
- If you have underlying health conditions like diabetes or arthritis, ensure they are well-managed to reduce CTS risk.
Living with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Living with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) involves several strategies to manage the condition and maintain hand comfort:
- Follow the treatment plan and advice your orthopaedic specialist provides, which may include splinting, medication, or lifestyle changes.
- Take prescribed medications as directed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Wear a wrist splint to support your wrist in a neutral position and reduce pressure on the median nerve if recommended.
- Be mindful of activities that worsen your symptoms, and consider modifications to reduce strain on your wrists.
- Engage in recommended exercises and physical therapy to improve hand strength and flexibility.
- Keep scheduled appointments with your orthopaedic specialist to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Be open to lifestyle changes that protect your wrists and minimise discomfort, especially during activities that involve repetitive hand movements.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist, causing pain, numbness, and discomfort. However, it can be effectively managed with the right approach and timely medical attention. It’s essential not to ignore your hand health and seek professional advice if you experience symptoms of CTS.
Suppose you or someone you know is dealing with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and is seeking expert care and consultation. In that case, we encourage you to request an appointment with The Orthopaedic Practice and Surgery Clinic. Their specialised team can provide personalised treatment and guidance, helping you regain full hand function and lead a more comfortable life. Don’t hesitate to take that proactive step toward a pain-free and fully functional hand—request your appointment today.